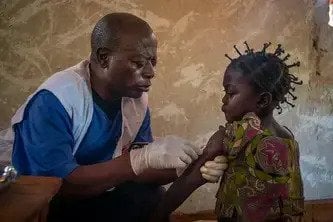
When the number of patients with confirmed COVID-19 began to rise in March 2020, the Philippines quickly put in place strict community quarantine measures. As of July 2020, there has been no local transmission in the southern city of Marawi, showing how these measures appear to have contributed to containing the new coronavirus.
However, they have also affected the livelihoods of the city’s residents, particularly displaced people living in and around Marawi.
Marawi is the only city in the Philippines with a Muslim majority in an otherwise overwhelmingly Catholic country.

Providing treatment during lockdown in the Philippines
“From the outset of the public health emergency, residents in Marawi observed precautionary measures very strictly, with the hope that the community quarantine would be lifted by the time Ramadan approached,” says Chika Suefuji, Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) project coordinator in Marawi. “However, the community quarantine continued, and people couldn’t go to their masjid or mosque, which is one of the most important practices during Ramadan.”
“Some people were understandably upset to learn that they had to observe Ramadan differently this year; some questioned this decision, since only a few cases of COVID-19 infections had been reported in the area,” continues Suefuji. “We discussed this with the community and religious leaders, explaining how the virus spreads. They understood well and put out a statement asking people to follow the safety measures.”
“This approach helped to disseminate accurate information and convinced a larger number of residents to follow the measures,” says Suefuji. “Overall, people have respected social orders to protect their families and communities, and it has helped contain the virus in the community.”
COVID-19 brought a lack of access to clean water and healthcare
While the COVID-19 pandemic has so far not hit the area severely, it has added extra burdens on to the people of Marawi. During the community quarantine, medical consultations at health facilities were suspended. The lack of access to clean water made following the recommendations to contain the spread of the virus particularly challenging.
Patients suffering from non-communicable diseases, such as hypertension or diabetes, were especially vulnerable to the virus. MSF teams carried out home visits to ensure patients continued to receive their medication and to provide patients with a leaflet about the virus and on how to protect themselves and their families from it.

Marawi under siege – and then in ruins
The city of Marawi came under siege in May 2017 by a group related to Islamic State group, which tried to take control of the city, resulting in a conflict erupting between the army and the group. The siege lasted five months and forced around 370,000 people to flee their homes.
More than three years later, parts of the city still lie in ruins. Around 70,000 people continue to live in harsh conditions in temporary shelters and another 50,000 are estimated to be living in other family members’ houses. They all have vivid memories of the siege. Thirty-four year old Ajibah Sumaleg recalls how her family had to flee their home with only a few days’ notice and returned to find it destroyed five months later.
Around 200,000 people live in Marawi, which is located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region of Muslim Mindanao (BARMM), in the south of the Philippines. The region is currently in transition to increase its autonomy from the Philippines. It has long struggled with the weakest health and economic indicators in the country and, since the end of the siege in October 2017, there have been outbreaks of measles, dengue and polio.
Before 2017, the political situation in the region was unstable, with regular conflicts between various armed groups. However, people there are hopeful that political changes will bring long-term stability and prosperity to the region.
Displaced living in difficult conditions
Initially, displaced people were provided with tents, until the evacuation centres and temporary shelters had been built. The last families moved from tents to the shelters only in January 2020.
Sobaida Comadug, 60, recalls how her husband died of a heart attack when the city was besieged. According to her, the shelters are not much better than the tents.
“We were told that these would be built to last for five years,” says Sobaida. “Do you think the government will build a longer-lasting shelter? No!”

Life as a displaced person in Marawi
She has spent all her life in Marawi. She describes the daily challenges which displaced people face.
Water is lacking, and the temporary shelters are far from the markets. Food is costly. All these factors push people to eat ready-to-eat meals, while doctors recommend healthy food to complement treatment for non-communicable diseases.
“It is more difficult to cook healthy meals,” says Sobaida. “We are far from the fruit and vegetable vendors, and even if we could reach them, we don't have clean water to wash them.”
The limited access to clean water creates hardships.
“The living conditions of the people are concerning. The water trucking saves lives, but is only a temporary measure as opposed to a long-term solution,” says Chika Suefuji. “I hope that the plight of internally displaced people in Marawi and Lanao del Sur becomes known and that leads to a better future for the people.”
MSF improves difficult access to healthcare
During the community quarantine in April and May, families faced tough decisions since most people were not able to work. People had to decide whether to use their money for the family’s food, or healthcare for a sick family member.
Even before the community quarantine, healthcare was difficult to obtain following the siege. Only 15 of the 39 health facilities in Marawi and the surrounding areas were functioning; the others had been destroyed or were unable to reopen. MSF rehabilitated four health centres after the siege to support communities in Marawi, and began providing clean drinking water and mental health services.
Non-communicable diseases were responsible for 41.5 per cent of deaths in the BARMM region in 2015. Hypertension and diabetes are among the 10 most prevalent diseases.
We currently support three health centres in the area, provide mental healthcare, treat non-communicable diseases, such as hypertension and diabetes, and provide free medication.

“It is critical for the people of Marawi, especially patients suffering from non-communicable diseases, that the spread of COVID-19 remains in check,” says Janoa Manganar, MSF medical team leader.
In the Philippines, surveillance and contact tracing activities for COVID-19 are also conducted at the community level. We have started to train teams in all 72 districts within Marawi city in how to conduct surveillance and contact tracing, and how to share information related to COVID-19 prevention, home quarantine and mental health together with the local health authority.
People living in Marawi face an uncertain future. The rehabilitation of the area in central Marawi that was destroyed during the siege continues to be a challenge because of the presence of the remnants of war, such as unexploded ordnance, among several other reasons.
Many still hope that political changes will bring positive change to their futures; however, the reality is that, almost after three years after the end of the siege, many people are still displaced from their homes, living in temporary shelters or in the homes of relatives, not knowing how long this will last.
The siege and the pandemic added to the worries of people in Marawi, says Sarah Oranggaga. She was forced to move in with her siblings again after having to give up her small corner store in Marawi. She says, “I am okay for now, and we just accept how things are and slowly we’ll overcome this.”