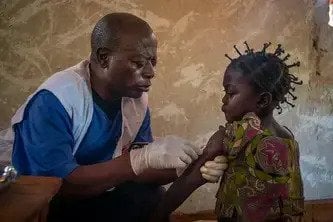
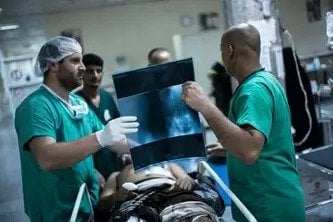
Ahead of the G7 summit in Hiroshima, Japan, Dr Christos Christou, International President of Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF), urges the leaders of G7 countries* to make a long-term commitment to safeguarding humanitarian assistance despite highly polarised conflicts and tensions across continents.
The name Hiroshima epitomises the price that civilians pay in conflict. Although very few single events can be compared to such a sudden and massive loss of life, civilians continue to be the main victims in wars and conflicts.
Since the Second World War, a set of legal instruments like International Humanitarian Law (IHL) were developed to protect civilians in conflict, yet governments still too often place other considerations like counter-terrorism, sovereignty, and migration policies above the protection of individuals in conflicts or fleeing them.
Every day, MSF witnesses the impacts of war and conflict on people’s lives: from physical and mental injuries to malnutrition, sexual violence and the destruction of entire medical infrastructures and healthcare systems. We see how surviving war in 2023 is in no way easier than it was 50 or even 70 years ago.

This was evident during the first hours of conflict in Sudan, when most of the wounded our medical teams received in El Fasher were civilians, among them many children. Hospitals had to close due to their proximity to the fighting, or because medical staff could not reach facilities due to the violence. With scarce surgical capacity and supplies running out, over 40 people died from their injuries within three days.
As violent conflict continues to take a heavy toll on civilians, IHL protections intended to safeguard civilians, infrastructure, and humanitarian workers are increasingly ignored or denied. Earlier this year, two of my colleagues were killed in an appalling attack against our humanitarian team working in Burkina Faso. In 2021, we lost three colleagues in Tigray, Ethiopia, to brutal murders that are still not fully explained. Providing humanitarian assistance to communities in need should never cost someone their life.
Obstruction and criminalisation of humanitarian assistance
MSF teams continue to claim the space to provide vital medical care wherever and whenever needs are greatest. This is our raison d’être. Yet principled and lifesaving humanitarian action has been increasingly obstructed by governments, including G7 countries, over the past 10 years.

On the Mediterranean Sea, one of the world’s deadliest migration routes for people fleeing violence, insecurity, and persecution, our search and rescue ships have been repeatedly detained, fined and unable to disembark survivors in safe ports. This year, the number of deaths at sea is reaching new records. Yet, new legislation by the Italian government created a new series of bureaucratic burdens leading to the detention of our ship, the Geo Barents, earlier this year.
The Italian and EU governments must stop criminalising migration and humanitarian assistance, and instead enable aid organisations like MSF to continue their lifesaving work, which these states should be carrying out in the first place.
Meanwhile, in Canada, anti-terror laws in place for over 20 years have never fully exempted humanitarian action, which means that – unbelievably – there has existed a risk that Canadian humanitarians could find themselves on the wrong side of the law while supporting people in crisis settings.
As Canada now looks to update its anti-terror legislation to facilitate international assistance in places where these laws apply, MSF calls on the Canadian government to uphold IHL and apply a full humanitarian exemption in its anti-terror laws. Humanitarian assistance must never be held back by laws intended to criminalise terrorism-related offences.
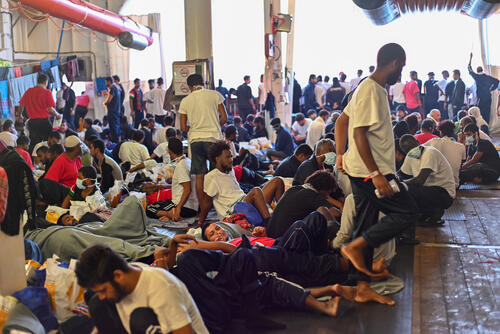
These are just two examples. The rising deaths of people on the move, the physical and administrative border walls, the abysmal reception or detention conditions in many places should be viewed by G7 countries as a humanitarian failure on their watch, often on their own borders.
Principled humanitarian actions
Humanitarian assistance must be delivered to those who need it the most, whatever side of a frontline they happen to be. Increasingly, however, this fundamental humanitarian principle is being challenged by legal frameworks, dangerous public narratives and actions on the ground converging to criminalise those trying to deliver relief.
There are existing UN resolutions (e.g. UN Security Council Resolution 2286 adopted in 2016) reinforcing the IHL to protect medical and humanitarian action, and others are in the making. But these have no value if political or counter-terrorism narratives and actions supersede these commitments. This will continue to risk intimidation, physical harm and imprisonment of those who are trying to deliver much-needed care. More fundamentally, it can erode the trust that communities need to have that humanitarians are just that, and ultimately drastically reduce people's access to the care they need.

Unfortunately, MSF knows all too well what happens when principled humanitarian action is called into question. Just last year, five of our colleagues endured months of unjustified incarceration in the conflict-affected region of Cameroon based on groundless accusations of complicity with secession. It took more than a year before they were acquitted. To this day, we are prevented from providing humanitarian aid as authorities have suspended our medical activities, depriving thousands of people of critical medical care.
Global humanitarian solidarity
In their communique preceding the summit, G7 foreign ministers made a clear and determined commitment to support “vulnerable populations severely affected by multiple crises,” including in Afghanistan, Haiti, Ukraine and beyond. These words ring hollow from G7 members who still too often stand in the way of lifesaving humanitarian action at and beyond their own borders.
To truly fulfill their humanitarian commitments, MSF calls on G7 leaders to safeguard civilians and humanitarian workers, including by promoting and protecting principled humanitarian action. This must also apply when it comes to military support to third countries. If the unthinkable tragedies at Hiroshima offer any reminder, it is that world leaders must never place politics over humanity. Today, just as it was yesterday, too much is at stake.
*G7 countries: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, United Kingdom, United States of America and representatives of the European Union.