Amsterdam - Independent humanitarian agencies remain largely blocked from accessing vulnerable communities in northern Rakhine, raising major concerns about unmet medical and humanitarian needs.
On 11 August 2017, two weeks prior to attacks by the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA) and the Myanmar Army’s so-called “clearance operations” that followed, Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) lost government authorisation to carry out medical activities in northern Rakhine. One year on, MSF remains unable to operate in the area.
“The lack of sustained independent assessments in northern Rakhine means that no one has a comprehensive picture of the situation on the ground and the medical and humanitarian needs,” says Benoit De Gryse, MSF’s operations manager for Myanmar.
MSF has repeatedly requested that the Myanmar government grant it the necessary travel and activity authorisations to provide medical care to those in need, but administrative red tape has made this impossible.
MSF once again requests the government grant immediate and unfettered access to northern Rakhine to all independent and impartial humanitarian actors, to ensure that the healthcare needs of the population can be evaluated and addressed.Benoit De Gryse, MSF operations manager for Myanmar
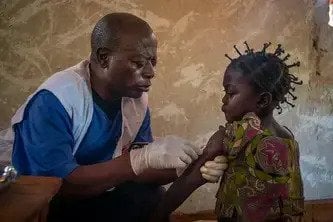
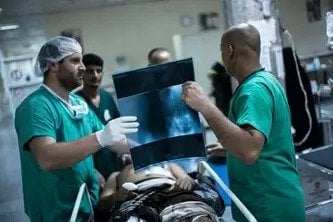
MSF has provided healthcare to all communities in northern Rakhine since 1994. At the time operations were suspended on 11 August 2017, MSF was operating four primary healthcare clinics in northern Rakhine – three of which were subsequently burnt down – and was providing over 11,000 primary and reproductive healthcare consultations per month, as well as emergency transport and assistance for patients requiring hospitalisation.
With over 700,000 Rohingya fleeing targeted violence in northern Rakhine from 25 August 2017 onwards, many areas have been depopulated. Yet there are still 550,000 to 600,000 stateless Rohingya across Rakhine state.
"The medical needs of the remaining Rohingya population in northern Rakhine, as well as those of ethnic Rakhine and other minorities, must be thoroughly and independently assessed,” says De Gryse.
MSF maintains staff presence in Maungdaw despite being unable to run medical activities, and our teams continue to hear from the Rohingya community there about the difficulties they face accessing healthcare. Muslim patients continue to face restrictions on their freedom of movement and unaffordable medical fees.
One person* MSF spoke to was forced to seek medical care in recent months for their mother in Bangladesh, who died there. “We don’t have access to Sittwe or Yangon so the only option is to cross the border to Bangladesh,” they told MSF. “This is a very risky route. If I could take my mother’s body back to my village and have a funeral next to my father, I would be very happy. But that is not going to happen due to the situation of my country. If we had been able to see a specialist here, we wouldn’t have had to go to Bangladesh.”
The Myanmar government has claimed that healthcare needs are being met, but the severe limitations on humanitarian access to northern Rakhine underline the lack of independent information on conditions.
“Humanitarian access is key to understanding the situation on the ground; without credible information there is no way to assess conditions for return,” says De Gryse.
*The identity of the person has been withheld at their request.
MSF continues to provide primary healthcare and emergency referrals for patients in Sittwe district, central Rakhine. Elsewhere in Myanmar, MSF continues to run medical projects in Shan, Kachin and Yangon, as well as in the Naga Self-Administered Zone and Tanintharyi region.
Addendum 01/09/2019:
While MSF staff have remained present in northern Rakhine State, it was only in September 2018, with the necessary government approvals, that MSF was able to re-establish a significantly reduced medical programme, with a focus on HIV support. Initial activities included HIV counselling training for hospital staff delivered in Buthidaung and Maungdaw hospitals.
Activity approvals to conduct mobile clinics with the Ministry of Health were granted for August 2019, with the first mobile clinic held three days a week in Buthidaung Downtown.
In Sittwe and neighbouring areas, MSF’s activities were put on hold on 25 August 2017. Travel and activity authorisations were received on the 12 October 2017, and the MSF team was able to re-establish regular activities, before returning to a normal schedule as of mid-October 2017.