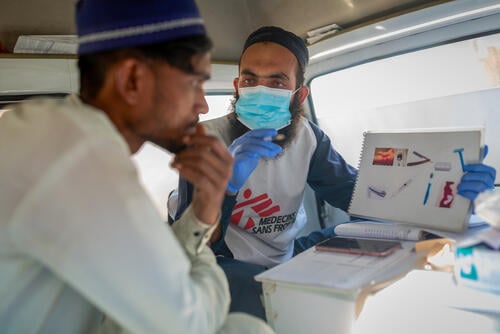
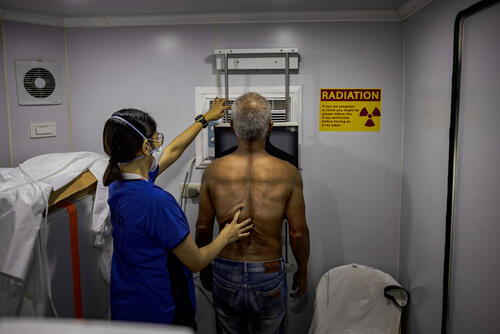
During the 1990s, MSF teams made a bitter observation: we were failing to treat some of our patients suffering from infectious diseases, while in developed countries, remarkable progress was being made in the field of health. Two decades on, medicines in developing countries are still either too expensive, aren't suitable to be used in many of the contexts in which we work (for example, in hot, humid conditions or where there's a lack of electricity), or simply don't exist for the diseases we need to treat.
In 1999, we launched the Campaign for Access to Essential Medicines, now known as the Access Campaign. Its mission focuses on three areas: overcoming barriers to access to essential medicines, stimulating research and development for neglected diseases, promoting health exceptions to global trade agreements.
In 2003, MSF joined several research institutes, including the Institut Pasteur, to create the Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi), a non-profit research and development organisation engaged in research and development of new treatments for neglected diseases.

Improved treatment options recommended by the World Health Organization

Out of Darkness: Fighting Hepatitis C in Ukraine

Pfizer and GSK’s HIV/AIDS division, ViiV, prevents children with HIV from getting needed medicine

Last-minute pressure to drop language on protecting access to affordable medicines from TB Summit declaration negotiations

Country takes landmark step for access to medicines

Access Campaign Year in Review 2017

Myanmar: treating HIV, TB, and hepatitis C in Insein clinic, Yangon

One year, 1,198 patients