Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) is an international, independent, private and non-profit organisation. It comprises 21 institutional members under the MSF International Statutes and 10 specialised organisations, which take charge of specific activities such as humanitarian relief supplies, epidemiological and medical research, and research on humanitarian and social action. As these organisations are controlled by MSF, they are included in the scope of the MSF Financial Report and the figures presented here. These figures describe MSF’s finances on a combined international level. The figures presented here are for the 2016 calendar year. All amounts are presented in millions of euros.
Figures in these tables are rounded, which may result in apparent inconsistencies in totals.
Largest country programmes based on expenditure
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- South Sudan
- Central African Republic
- Yemen
- Iraq
- Haiti
- Syria
- Nigeria
- Ethiopia
- Niger
The total expenditure for our programmes in these 10 countries is 534.8 million euros, 54 per cent of MSF’s operational expenses.
MSF staff
Staff figures represent total full-time equivalent positions.
Where did the money come from?
Thanks to 6.1 million private donors.
Year-end financial position
In millions of euros
| Assets | 2016 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|
| Non-current assets | 228.9 | 98.9 |
| Other current assets | 222.6 | 175.9 |
| Cash and equivalents | 1,101.1 | 1,024.7 |
| Liabilities and funds | 2016 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|
| Current liabilities | 239 | 168.1 |
| Unrestricted funds | 1,107.4 | 1,059.8 |
| Restricted funds | 35.9 | 15.6 |
| Other funds | 70.3 | 56 |
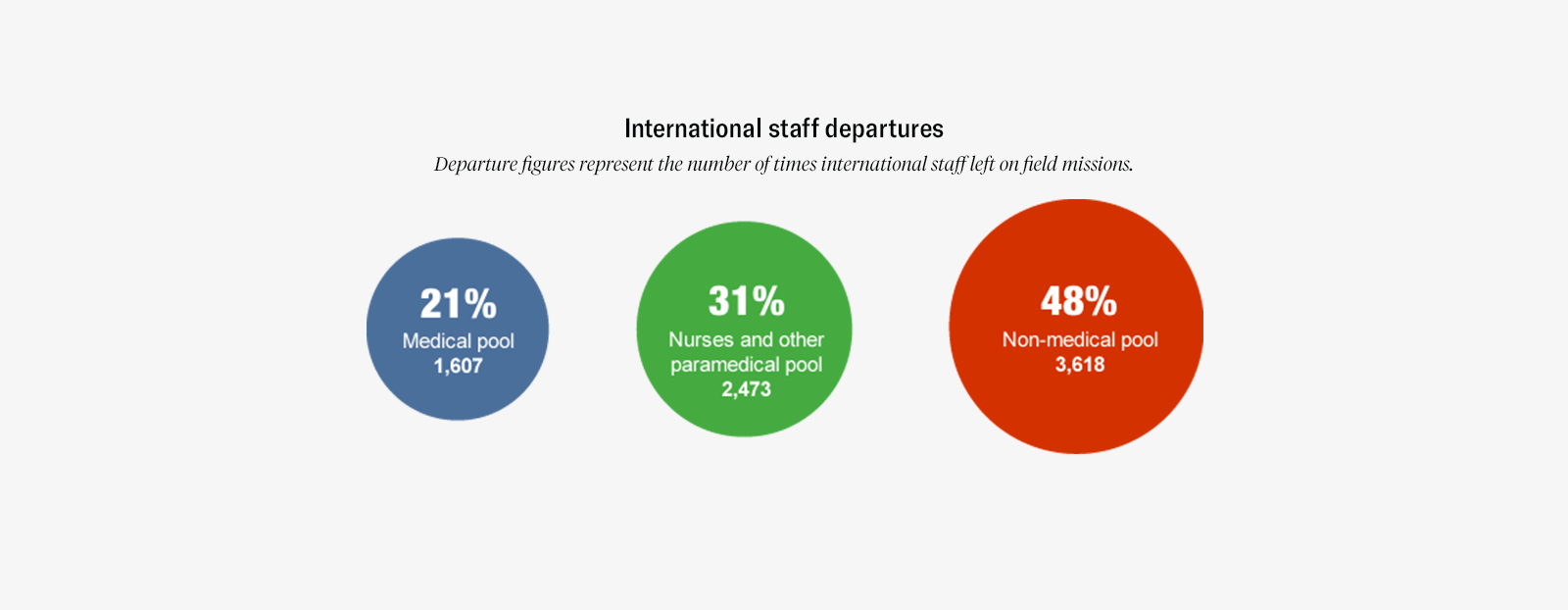
The majority of MSF staff (83 per cent) are hired locally in the countries of intervention. Headquarters staff represent 9 per cent of total staff. Departure figures represent the number of times international staff left on field missions. Staff figures represent the total full-time equivalent positions.
Sources of income
As part of MSF’s effort to guarantee its independence and strengthen the organisation’s link with society, we strive to maintain a high level of private income. In 2016, 95 per cent of MSF’s income came from private sources. More than 6.1 million individual donors and private foundations worldwide made this possible. Public institutional agencies providing funding to MSF included, among others, the Humanitarian Aid Office of the European Commission (ECHO) and the governments of Belgium, Germany, Denmark, Canada, Spain, Norway, Japan, Luxembourg, Holland, Ireland, Sweden and Switzerland.
Expenditure
Expenditure is allocated in line with the main activities performed by MSF according to the full cost method. Therefore all expense categories include salaries, direct costs and allocated overheads (e.g. building costs and depreciation).
Programme expenses
Programme expenses represent expenses incurred in the field or by headquarters on behalf of the field.
Other expenses
Other expenses comprises costs associated with raising funds from all possible sources, the expenditures incurred in the management and administration of the organisation, as well as income tax paid on commercial activities.
Permanently restricted funds
Permanently restricted funds may be capital funds, where donors require the assets to be invested or retained for long-term use rather than expended; or the minimum compulsory level of retained earnings to be maintained in some countries.
Temporarily restricted funds
Temporarily restricted funds are unspent designated donor funds to a specific purpose (e.g. specific country or project), restricted in time, or required to be invested and retained rather than expended, but without any contractual obligation of reimbursement.
Unrestricted funds
Unrestricted funds are unspent, non-designated donor funds expendable at the discretion of MSF’s trustees in furtherance of our social mission.
Other funds
Other funds are foundations’ capital and translation adjustments arising from the translation of entities’ financial statements into euros.
MSF’s funds have been built up over the years by surpluses of income over expenses. At the end of 2016, the available portion (excluding permanently restricted funds and capital for foundations) represented 9.2 months of the preceding year’s activity. The purpose of maintaining funds is to meet the following needs: working capital needs over the course of the year, as fundraising traditionally has seasonal peaks while expenditure is relatively constant; swift operational response to humanitarian needs that will be funded by forthcoming public fundraising campaigns and/or by public institutional funding; future major humanitarian emergencies for which sufficient funding cannot be obtained; the sustainability of long-term programmes (e.g. antiretroviral treatment programmes); and a sudden drop in private and/or public institutional funding that cannot be matched in the short term by a reduction in expenditure.
Find out more about MSF Financial Report
They represent an aggregation of the Financial Statements of the 21 institutional members under MSF International statutes (Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany, Greece, Holland, Hong Kong, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Norway, South Africa, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, the United Kingdom and the United States), together with the Financial Statements of offices in Argentina, the Czech Republic, Republic of Korea, India and Ireland, satellite organisations (MSF Supply, MSF Logistique, Epicentre, Fondation MSF, Etat d'Urgence Production, MSF Assistance, SCI MSF, SCI Sabin, Fondation MSF Belgique, Ärzte Ohne Grenzen Foundation and MSF Enterprises Limited) and MSF International.