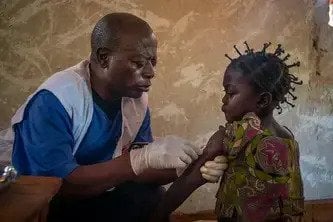
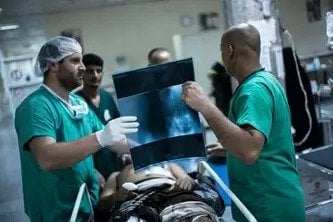
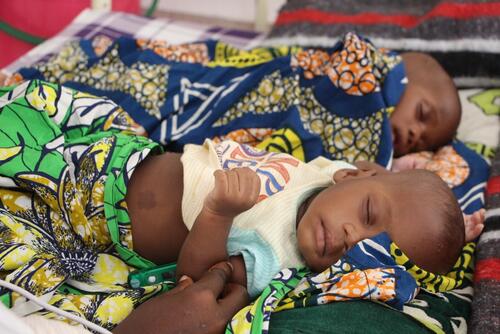
- Displaced people in Monguno, Borno State, are living in poor conditions, with little sanitation and a lack of safe drinking water.
- There is an urgent need for better coordination between the Nigerian government, United Nations and non-governmental organisations in scaling up the aid response.
- With the rainy season on its way, shelter, water, sanitation, food, protection and medical care must be scaled up urgently to avoid a catastrophe.
Over 30,000 people who were forced to flee to the town of Monguno, following renewed clashes that erupted in Nigeria’s Borno state in late December 2018, are in acute need of shelter, water, sanitation, food, protection, medical care and mental health support, warns Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF).
People’s immediate humanitarian needs are not being adequately addressed, and there is an urgent need for better coordination between the Nigerian government, United Nations and non-governmental organisations in scaling up the aid response in Monguno. It is critical to avoid a catastrophic situation with the onset of the rainy season, expected in May.
People are sleeping on the streets or wherever they can find space, hungry, thirsty and exposed to very high temperatures during the day and low temperatures at night.Musa Baba, MSF humanitarian affairs officer
For the last ten years, people in Borno state have been caught up in a cycle of violence, displacement, and insecurity. People’s health are at risk due to the dire living conditions. The latest clashes have yet again forced tens of thousands from their homes, fields and livelihoods, and left them struggling to survive.
“People who recently arrived in Monguno fled their homelands leaving everything behind,” says MSF humanitarian affairs officer Musa Baba. “They come from areas where they could farm. Now, they are sleeping on the streets or wherever they can find space, hungry, thirsty and exposed to very high temperatures during the day and low temperatures at night.”
A major problem in Monguno is the lack of land to build shelters for new arrivals. Thousands of recently displaced people have no space to settle and are living and sleeping in the middle of the town’s streets for weeks, even months. MSF, along with some other humanitarian organisations, have built shelters in different camps and have capacity to accommodate more displaced people. Our teams have set up 100 tents and are ready to put up 700 additional shelters.
“The current situation, with very vulnerable people – women, children and the elderly – living out of doors, rather than in a camp or with the host community, increases the risk of abuse and the need for protection,” says Musa.
We are surviving by doing menial jobs like washing dishes and getting paid for it.Hajja Bukar, recently arrived displaced person in Monguno
Hajja Bukar, aged 35, recently arrived in Monguno, having been displaced a number of times already over recent years due to the conflict. She and her four children have settled in one of the town’s camps for displaced people, in a rudimentary shelter made of sticks and cloth.
“We are surviving by doing menial jobs like washing dishes and getting paid for it,” says Hajja. “Our men sometimes go into the bush to fetch firewood to sell.”
Poor living conditions, with little sanitation and a lack of safe drinking water are putting displaced people in Monguno at risk of pneumonia, diarrhoea and malaria, among other preventable diseases. With few latrines, most people use open defecation areas, which are likely to flood in the rainy season, worsening the health conditions.
MSF is running a 10-bed emergency room for adults in a ministry of health facility in Monguno as well as providing people with mental health support. Following an accidental fire in Stadium camp for displaced people in February, where 850 displaced families are sheltering, we distributed 500 kits of essential relief items including mats, tarpaulins, blankets, jerrycans, cooking equipment and hygiene items.
MSF has been working in Nigeria since 1996 and has had a permanent presence in Borno state since 2014. Our teams provide lifesaving medical care in northeastern Nigeria, running projects in Gwoza, Maiduguri, Monguno, Ngala, Pulka and Damaturu, while our emergency teams respond to disease outbreaks and other urgent humanitarian needs.